Top Nifty Gainers
In the ever-evolving world of finance, the Nifty Index emerges not just as a benchmark but as a storyteller, narrating the vibrant saga of the Indian economy. This prestigious index, a composite of top-performing stocks, serves as a crucial barometer for investors and market analysts worldwide. Its fluctuations and trends offer a window into the underlying forces shaping the economic and corporate landscape of India. In this article, we embark on an insightful expedition to unravel the mysteries of the Nifty Index. Our focus is not only on identifying the top gainers that have led the charge in Nifty’s remarkable journey, but also on understanding the broader market dynamics and sectoral shifts that have propelled these trailblazers to prominence.
As we delve into the intricacies of market movements, investment strategies, and future projections, our narrative aims to be an enlightening guide for both seasoned investors and enthusiastic newcomers to the financial arena. We will explore the vital indicators that signal a stock's potential for growth, the strategic manoeuvres of successful companies, and the impact of global economic trends on the Indian market.
Furthermore, this article will illuminate the challenges and risks inherent in navigating the turbulent waters of stock investing, providing a balanced view of the high-reward, high-risk nature of the stock market. Our journey through the Nifty Index is designed to offer a panoramic view of the factors driving its top performers, equipping readers with the knowledge and insights needed to understand and participate in the dynamic world of stock investing.
Decoding the Nifty Index
The Nifty 50, an emblem of India's burgeoning financial landscape, is more than just an index; it's a reflection of the country's economic heartbeat. Comprising 50 of the largest and most actively traded stocks on the National Stock Exchange (NSE), the Nifty 50 serves as a critical indicator of the Indian stock market's health and direction. This index, often used by investors and financial professionals as a benchmark, encapsulates a wide spectrum of sectors, representing the diversity and dynamism of India’s corporate sector.
Understanding the Composition: The Nifty 50 is meticulously crafted to provide a balanced representation of the Indian economy. Its constituents are selected based on their market capitalization, liquidity, and trading frequency. These criteria ensure that the index accurately mirrors the performance of the Indian market and remains relevant to investors seeking to understand or invest in Indian equities. The index is weighted by free-float market capitalization, meaning that only shares available to the public are considered, providing a more accurate gauge of market movements.
Sectoral Diversity: One of the strengths of the Nifty 50 lies in its diversified sectoral coverage. It spans across major sectors such as financial services, IT, consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, and more. This diversity not only mitigates sector-specific risks but also offers a comprehensive view of the Indian economy's overall health. By tracking the Nifty 50, one can gauge the economic trends and shifts in consumer patterns, technological advancements, and policy changes affecting these sectors.
Historical Performance and Trends: Historically, the Nifty 50 has been a witness to the Indian economy's highs and lows, reflecting macroeconomic changes, global events, and domestic shifts. The index has seen periods of robust growth, marked by investor optimism and economic stability, as well as phases of volatility, driven by global uncertainties and internal economic challenges. Analyzing these trends provides valuable lessons in market resilience and the cyclical nature of stocks.
The Nifty 50's Rebalancing: The index is not static; it undergoes periodic rebalancing to ensure it continues to reflect the current state of the Indian stock market. This rebalancing, done semi-annually, takes into account changes in market capitalization and stock performance. Such adjustments are crucial as they keep the index relevant and prevent it from being skewed by the disproportionate influence of any single stock or sector.
Impact of Global Events: In today's interconnected world, global events significantly influence the Nifty 50. Be it geopolitical tensions, global financial crises, or pandemics like COVID-19, their impact resonates through the index. Investors closely watch these events, as they often trigger market volatility and offer both risks and opportunities. The Nifty's response to these events is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the Indian market.
In conclusion, the Nifty 50 is more than a mere collection of stocks; it's a barometer for India's economic and financial health. Its composition, diversified across various sectors, offers a unique perspective into the intricacies of the Indian market. For anyone looking to understand the dynamics of Indian stocks, the Nifty 50 provides a foundational understanding, reflecting both the opportunities and challenges within one of the world's fastest-growing economies. As we move forward, the Nifty 50 will continue to be a critical tool for investors, analysts, and policymakers alike, providing insights and guiding investment strategies in the vibrant landscape of the Indian stock market.
The Dynamics of Stock Gains
Understanding the dynamics behind stock gains is crucial for any investor looking to navigate the complexities of the stock market, particularly when focusing on indices like the Nifty 50. Stock prices are influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from company-specific news to global economic trends, each playing a pivotal role in the ascent or decline of stock values.
Fundamental Factors Driving Stock Prices: At the core of stock gains are fundamental factors, which include a company’s financial health, earnings, growth potential, and management efficiency. A company reporting robust earnings and promising future prospects often sees an uptick in its stock price. Investors value firms with strong balance sheets, low debt, and high profitability, as these traits indicate stability and potential for future growth. Additionally, management's effectiveness in navigating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities can significantly sway investor confidence, impacting stock prices.
Market Sentiment and Investor Perception: Beyond fundamentals, market sentiment plays a critical role. This sentiment is shaped by how investors perceive various factors, including political climate, economic policies, and sectoral trends. Positive sentiment, often driven by optimism about future growth and stability, can lead to stock gains, while negative sentiment, fueled by uncertainty or adverse events, can cause prices to fall. Sentiment is often a reflection of collective investor psychology, making it a powerful yet sometimes unpredictable force in the market.
Impact of Economic Indicators: Economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and employment data also influence stock prices. For instance, high inflation or interest rates can dampen stock gains, as they may lead to increased costs and reduced consumer spending. Conversely, favorable economic data, indicating a healthy economy, can boost investor confidence, leading to stock gains. These indicators are particularly relevant in emerging markets like India, where economic growth can have a pronounced impact on market sentiment and stock performance.
Global Events and Their Influence: In today’s globalized world, international events have a significant impact on stock markets. Issues like trade wars, geopolitical conflicts, and global financial crises can lead to volatility in the stock market. For instance, a global event causing supply chain disruptions can negatively impact companies’ dependent on global trade, leading to a decline in their stock prices.
The Role of Institutional Investors: Institutional investors, such as mutual funds, pension funds, and hedge funds, also influence stock prices through their investment decisions. Their large-scale buying or selling can lead to significant movements in stock prices. The strategies and outlooks of these investors are closely monitored by the market, as they can provide insights into future trends and potential stock gains.
Technological Advancements and Stock Gains: Technological advancements and innovations can lead to significant stock gains, especially in sectors like IT, biotechnology, and renewable energy. Companies that innovate and adapt to new technologies often see an increase in their stock value, as investors anticipate future growth driven by these advancements.
In conclusion, the dynamics of stock gains are a complex interplay of multiple factors. Understanding these dynamics requires not only a grasp of the fundamental aspects of companies and economic indicators but also an awareness of broader market sentiment and global events. For investors in the Nifty 50 and beyond, this multifaceted approach is essential for making informed investment decisions and capitalizing on the opportunities presented by the ever-changing stock market landscape.
Sector Analysis: Where the Gainers Thrive
The Nifty 50, renowned for its broad market representation, is a melting pot of diverse sectors, each contributing uniquely to the index's performance. Understanding the dynamics of these sectors is crucial for investors looking to pinpoint where the top gainers thrive. This comprehensive sector analysis delves into the key industries within the Nifty 50, exploring their performance, growth drivers, challenges, and future prospects.
- Financial Services:
- Overview and Performance: This sector, often a heavyweight in the Nifty 50, includes banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and insurance companies. Historically, it has been a significant contributor to the index's gains, reflecting the growing importance of financial services in India's economy.
- Growth Drivers: Liberalization policies, increasing consumer demand for credit, and technological advancements in digital banking and fintech are pivotal growth drivers.
- Challenges and Future Outlook: Regulatory changes, non-performing assets (NPAs), and economic cycles greatly impact this sector. The future looks promising with the increasing penetration of financial services in rural areas and the rise of digital transactions.
- Information Technology (IT):
- Overview and Performance: A stellar performer in the Nifty 50, the IT sector represents India’s prowess in software services and consulting.
- Growth Drivers: Global demand for IT services, digital transformation, and India's competitive advantage in software services fuel growth.
- Challenges and Future Outlook: The sector faces challenges like currency fluctuations and global economic conditions. However, the ongoing digital revolution and emerging technologies like AI and cloud computing offer immense growth potential.
- Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare:
- Overview and Performance: This sector includes pharmaceutical companies, healthcare services, and biotechnology firms. It has seen varying performance, often influenced by global and domestic health policies.
- Growth Drivers: Increasing global demand for generic medicines, India's cost-effective manufacturing, and a growing domestic market drive this sector.
- Challenges and Future Outlook: Regulatory scrutiny, particularly from international bodies like the FDA, and competition in the generics market are key challenges. The sector's future is bright with opportunities in biotechnology and increased healthcare spending.
- Consumer Goods and Retail:
- Overview and Performance: Encompassing a wide range of companies, from food and beverages to household products, this sector is a reflection of domestic consumption trends.
- Growth Drivers: Rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and changing consumer preferences spur growth.
- Challenges and Future Outlook: Challenges include rural market penetration and competition from global brands. The sector is poised for growth with the expansion of organized retail and e-commerce.
- Automobile and Ancillaries:
- Overview and Performance: This sector represents a significant portion of India's manufacturing base, including vehicle manufacturers and component suppliers.
- Growth Drivers: Economic growth, rising middle-class incomes, and evolving consumer preferences drive demand.
- Challenges and Future Outlook: The sector grapples with regulatory changes, like emission norms, and fluctuating raw material prices. The future holds potential with the advent of electric vehicles and increased export opportunities.
In each of these sectors, the top gainers have been those companies that have successfully navigated the challenges, capitalized on the growth drivers, and innovatively adapted to changing market conditions. Their performances have been a testament to strategic foresight, operational efficiency, and adaptability.
Cross-Sectoral Analysis and Synergies:
- Interdependence Among Sectors: The performance of one sector often influences others. For example, growth in the IT sector can drive demand in the consumer goods sector through increased disposable incomes.
- Emerging Trends and Opportunities: Identifying cross-sectoral trends, like the impact of digital transformation across sectors, is crucial for investors.
- Synergies and Collaborations: Collaborations between sectors, such as between IT and healthcare for telemedicine, create new growth avenues.
Impact of Global Trends on Sector Performance:
- Influence of Global Economic Conditions: Economic conditions in key markets like the US and Europe significantly affect sectors like IT and pharmaceuticals.
- Trade Policies and their Implications: Trade policies, including tariffs and trade agreements, can impact sectors like automobile and consumer goods.
- Adapting to Global Standards and Practices: Compliance with global standards can be both a challenge and an opportunity for sectors like pharmaceuticals and IT.
Government Policies and Sectoral Growth:
- Impact of Economic Reforms: Economic reforms, such as GST and FDI policies, have a profound impact on sectors like retail and manufacturing.
- Sector-specific Policies: Policies like ‘Make in India’ for manufacturing and digital initiatives for IT and banking significantly influence these sectors.
- Navigating Regulatory Landscapes: Adherence to regulatory requirements is key for sectors like pharmaceuticals and financial services.
Innovation and Technology as Growth Catalysts:
- Role of Technology Across Sectors: Technology is a unifier across sectors, driving efficiency and creating new business models.
- Innovation as a Competitive Edge: Companies that innovate, whether in product development or service delivery, often emerge as gainers.
- Investing in Future Technologies: Sectors like automobile with electric vehicles and IT with cloud computing are investing in future technologies for sustained growth.
Sustainability and ESG Factors:
- Increasing Relevance of ESG Factors: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are becoming critical in investment decisions, impacting sectors differently.
- Sustainable Practices as a Differentiator: Companies adopting sustainable practices are increasingly favored by investors.
- Impact on Sectoral Performance: Sectors like energy and manufacturing are under scrutiny for environmental impacts, pushing them towards sustainable practices.
In conclusion, the analysis of these sectors within the Nifty 50 reveals a tapestry of interconnected industries, each with its unique challenges and opportunities. The top gainers in these sectors are those that have not only excelled in their respective fields but also embraced technological advancements, adapted to changing market conditions, and aligned with global trends and sustainable practices. For investors, understanding these sectoral dynamics is crucial in identifying potential gainers and making informed investment decisions in the vibrant and diverse landscape of the Indian stock market.
Smart Investment Strategies
Investing in the stock market, particularly in dynamic indices like the Nifty 50, requires more than just a basic understanding of stock movements. It necessitates a strategic approach, combining thorough research, risk management, and a keen eye for market trends. In this comprehensive guide, we explore smart investment strategies that can help investors navigate the complexities of the stock market and identify potential gainers.
- Understanding Market Fundamentals:
- Core Principles: Successful investing starts with a solid grasp of market fundamentals. This includes understanding key financial ratios, company earnings reports, and industry trends.
- Research and Analysis: Thorough research and analysis of companies and sectors give investors an edge. This involves studying financial statements, management quality, and market position.
- Identifying Potential Gainers:
- Growth Prospects: Look for companies with strong growth prospects. This includes those in emerging industries or those developing new technologies or products.
- Performance Metrics: Analyze performance metrics like earnings growth, return on equity, and profit margins. Consistent performance is often an indicator of a potential gainer.
- Diversification: A Key to Risk Management:
- Spreading Investments: Diversification across sectors and asset classes can reduce risk. Avoid putting all your capital in a single stock or sector.
- Balanced Portfolio: Maintaining a balanced portfolio, including a mix of growth and value stocks, can provide stability and growth potential.
- The Role of Technical Analysis:
- Price and Volume Trends: Technical analysis, which involves studying price and volume trends, can provide insights into market sentiment and potential stock movements.
- Using Technical Indicators: Tools like moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) can help in timing the market.
- Timing the Market vs Time in the Market:
- Market Timing Challenges: While timing the market can be rewarding, it is often challenging and risky.
- Long-Term Investment: Generally, a long-term investment approach yields better returns. It involves investing in fundamentally strong stocks and holding them over an extended period.
- Monitoring Macro and Micro Economic Indicators:
- Macro Indicators: Keep an eye on macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates as they can significantly impact the market.
- Micro Indicators: Company-specific indicators, including earnings announcements, management changes, and industry news, are crucial for stock selection.
- Leveraging Stop Loss and Profit Targets:
- Risk Management: Using stop loss and profit targets can help in managing risk and protecting gains. It prevents emotional decision-making and locks in profits.
- The Importance of Portfolio Review and Rebalancing:
- Regular Review: Regularly reviewing and rebalancing your portfolio ensures it aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Adapting to Changes: Be adaptable to market changes. If a sector or stock is consistently underperforming, it may be time to reallocate your investments.
- Staying Informed and Continual Learning:
- Keeping Updated: Stay informed about market developments, policy changes, and global events. Financial news, reports, and analyses are valuable resources.
- Ongoing Education: The market is ever-evolving, and so should your knowledge. Continuous learning through courses, webinars, and seminars is essential.
- Avoiding Common Pitfalls:
- Emotional Investing: Avoid emotional decisions; stick to your investment plan.
- Following the Herd: Don’t follow the herd; base your decisions on research and analysis.
- Overtrading: Frequent buying and selling can lead to higher costs and lower returns.
- Seeking Professional Advice:
- Professional Guidance: For those new to investing or with significant capital, seeking advice from financial advisors can be beneficial. They can provide tailored investment strategies based on your financial goals.
In conclusion, smart investment in the Nifty 50 or any other stock index requires a multifaceted approach. It involves understanding market fundamentals, diversifying investments, using technical analysis, timing the market judiciously, monitoring economic indicators, setting stop loss and profit targets, regularly reviewing the portfolio, staying informed, avoiding common pitfalls, and seeking professional advice when necessary. By adhering to these strategies, investors can enhance their chances of identifying potential gainers and achieving long-term financial success in the stock market.
Navigating the Challenges
Investing in the stock market, such as the Nifty 50, is not without its challenges. Understanding and navigating these hurdles is crucial for investors seeking to protect their investments and optimize returns. Here, we explore the key challenges faced in stock market investing and strategies to effectively navigate them.
- Market Volatility:
- Nature of Volatility: Stock markets are inherently volatile, with prices fluctuating due to various factors like economic news, corporate earnings, and global events.
- Managing Volatility: Diversification across sectors and asset classes can mitigate the impact of volatility. Long-term investment strategies also help in riding out short-term market fluctuations.
- Economic Cycles and Their Impact:
- Economic Fluctuations: The stock market is sensitive to economic cycles, including periods of growth, recession, and recovery.
- Adaptive Strategies: Aligning investment strategies with economic cycles, such as focusing on defensive stocks during recessions, can be beneficial.
- Impact of Geopolitical Events:
- Global Influences: Geopolitical events like elections, trade wars, and international conflicts can create uncertainty in the market.
- Informed Decisions: Staying informed about global events and understanding their potential impact on different sectors is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
- Overvaluation Risks:
- Assessing Valuations: Overvaluation occurs when stock prices exceed their intrinsic value, often leading to corrections.
- Valuation Metrics: Utilizing valuation metrics like price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and price-to-book (P/B) ratio helps in identifying overvalued stocks and avoiding potential losses.
- Regulatory Changes and Compliance:
- Regulatory Environment: The stock market is subject to regulatory changes that can impact investment strategies.
- Staying Compliant: Keeping abreast of regulatory updates and ensuring compliance is essential to avoid legal complications and capitalize on opportunities arising from regulatory shifts.
- Technological Disruptions and Sectoral Shifts:
- Evolving Technologies: Rapid technological advancements can disrupt traditional business models, impacting stock performance.
- Adaptation and Innovation: Investing in companies that are adapting to or leading technological innovations can offer growth opportunities. Monitoring sectoral shifts due to technology is also crucial.
In conclusion, navigating the challenges in stock market investing requires a combination of vigilance, adaptability, and informed decision-making. Understanding market volatility, aligning with economic cycles, staying abreast of geopolitical events, being wary of overvaluation, complying with regulatory changes, and adapting to technological disruptions are key to successful investing. By addressing these challenges head-on with a strategic approach, investors can safeguard their investments and capitalize on the opportunities that arise in the dynamic landscape of the stock market.
Sector-Wise Contribution to the Nifty 50
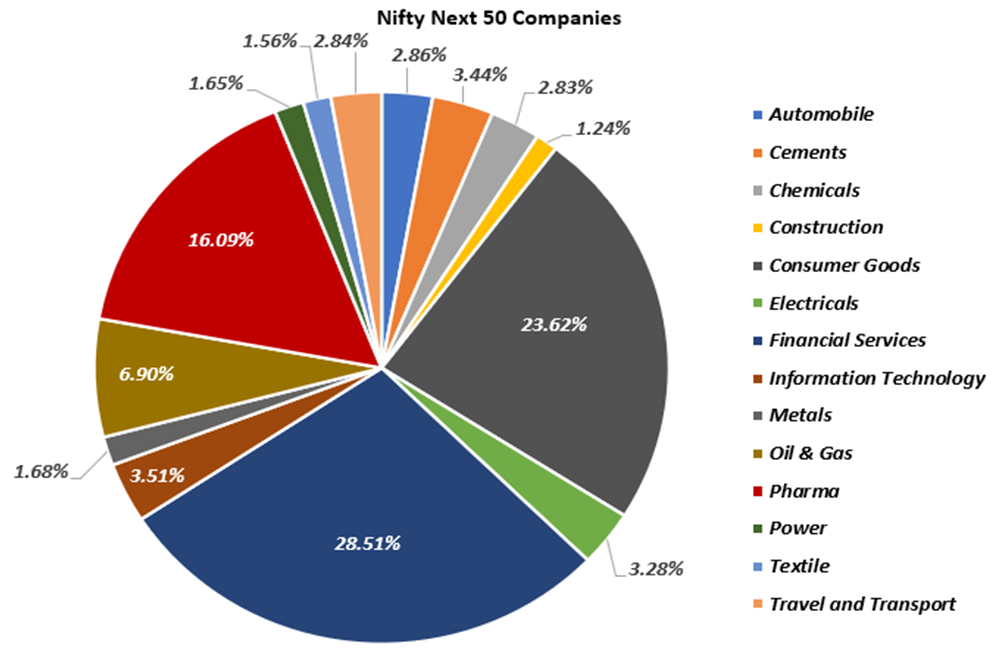
The above pie chart depicts the sector-wise weightage of companies within the Nifty Next 50 index. Here's a detailed analysis based on the visual data presented:
- Information Technology (IT) Sector: With a significant 28.51% share, IT is the dominant sector in the Nifty Next 50. This substantial proportion underscores the pivotal role of technology companies in the index and reflects the sector's rapid growth and importance in the Indian economy.
- Financial Services Sector: The second most substantial sector, with a 23.62% weightage, is Financial Services. This includes banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and insurance companies. The sector's prominence in the index highlights the depth and development of India's financial sector.
- Consumer Goods Sector: Holding a notable 16.09% share, the Consumer Goods sector represents a wide array of companies that produce goods used by consumers. This sector's sizeable portion indicates a robust domestic consumption market and the potential for growth driven by India's large population.
- Automobile Sector: This sector accounts for 6.90% of the Nifty Next 50. It includes manufacturers of cars, motorcycles, and commercial vehicles, as well as auto ancillaries. The sector's weight reflects its importance as a significant contributor to India's manufacturing output.
- Pharma Sector: Pharmaceutical companies have a 3.51% share in the index. The sector's presence marks the importance of healthcare and pharmaceuticals in the Indian market, especially considering India's role as a major global supplier of generic drugs.
- Metals Sector: With 3.28%, the Metals sector's weightage indicates its role in India's industrial growth and its significance as a basic industry in the economy.
- Oil & Gas Sector: This sector has a 2.86% weightage, showing the importance of energy companies in the market, which are crucial for the country's energy security and economic development.
- Cements Sector: The Cements sector represents 2.84% of the index, highlighting the ongoing infrastructure and construction development in the country.
- Chemicals Sector: With 2.83%, the Chemicals sector includes companies that produce industrial chemicals, fertilizers, and other chemical-based products, reflecting the diversity of India's industrial base.
- Electricals Sector: At 2.44%, the Electricals sector includes companies that manufacture electrical equipment, a critical component of infrastructure and consumer products.
- Power Sector: This sector, with a 1.68% share, includes companies involved in power generation and distribution.
- Textile Sector: Holding a 1.65% share, the Textile sector's weightage reflects its traditional significance and export potential.
- Travel and Transport Sector: This sector's 1.56% signifies the role of logistics, transportation, and related services in the economy.
- Construction Sector: With a 1.24% weightage, the Construction sector's presence acknowledges its importance in urbanization and infrastructure growth.
The pie chart's distribution of percentages indicates not only the sectoral composition of the Nifty Next 50 but also points towards the diverse nature of the Indian economy. The heavy weighting towards IT and Financial Services suggests a modern, service-oriented economy with strong consumer demand reflected in the Consumer Goods sector. The smaller percentages allocated to sectors like Construction and Textiles may indicate a smaller presence in the index, but not necessarily their overall impact on the economy, as these sectors are significant employment generators.
Comparison of Investment Strategies in nifty trading
|
Investment Strategy |
Description |
Risk Level |
Expected Return |
Time Horizon |
Suitability for Nifty Trading |
|
Long-term Buy and Hold |
Investing in Nifty 50 ETFs or Index Funds and holding them for an extended period. |
Low |
Moderate |
Long-term (5+ years) |
Suitable for passive investors who believe in the long-term growth of the Indian economy. |
|
Swing Trading |
Capitalizing on the short- to medium-term price swings in the Nifty 50. |
Medium |
Moderate to High |
Short to Medium-term (Days to Months) |
Suitable for active traders who can dedicate time to market analysis and timing. |
|
Day Trading |
Buying and selling Nifty 50 stocks within the same trading day to profit from intra-day price movements. |
High |
Variable (can be negative) |
Intra-day |
Suitable for full-time traders with a deep understanding of technical analysis and market indicators. |
|
Technical Analysis |
Using historical price patterns and charting tools to predict future movements of Nifty 50 stocks. |
Medium to High |
Moderate to High |
Variable |
Suitable for those who base their trades on technical indicators and chart patterns. |
|
Fundamental Analysis |
Selecting Nifty 50 stocks based on fundamental economic and financial analysis to hold until their value is realized. |
Low to Medium |
Moderate to High |
Long-term |
Suitable for investors who prefer to analyze company and economic fundamentals for long-term growth. |
|
Options Trading |
Using Nifty 50 index options to speculate or hedge against future price movements. |
High |
High (speculative) |
Short to Medium-term |
Suitable for knowledgeable traders familiar with options strategies and their risks. |
|
Arbitrage |
Exploiting the price differences of Nifty 50 stocks across different markets or forms. |
Low |
Low to Moderate |
Short-term |
Suitable for investors with the means to simultaneously trade in multiple markets or instruments. |
|
Algorithmic Trading |
Implementing computer algorithms to automate trading based on predefined criteria on Nifty 50 stocks. |
Medium to High |
High |
Variable |
Suitable for traders with technical expertise to create and backtest trading algorithms. |
|
Diversification across Sectors |
Investing across different sectors within the Nifty 50 to spread risk. |
Low to Medium |
Moderate |
Long-term |
Suitable for investors looking for sectorial exposure within the Nifty 50 to mitigate unsystematic risk. |
|
Momentum Investing |
Following the trend where traders buy Nifty 50 stocks that have been rising and sell those that are falling. |
Medium to High |
High |
Short to Medium-term |
Suitable for traders who believe in the continuation of trends and can manage the risk of trend reversals. |
This table outlines general strategies and their typical characteristics when applied to Nifty trading. It's important to note that all forms of trading carry risk and past performance is not indicative of future results. The suitability for Nifty trading column provides a brief idea of who might be best suited for each strategy, particularly within the context of the Nifty market. Investors should consider their own circumstances and, where appropriate, seek professional advice before engaging in Nifty trading.
Future Projections and Trends
As we look towards the horizon of India's financial markets, several key projections and trends are expected to shape the trajectory of the Nifty 50. Technological advancements and digitalization are poised to continue as significant growth drivers, particularly in the IT and financial services sectors, which currently hold robust positions within the index. The adoption of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain is anticipated to propel productivity and innovation, potentially leading to increased profitability for companies within these sectors.
Demographic trends such as a growing middle class, coupled with rising internet penetration and smartphone usage, are likely to bolster consumer-oriented sectors such as consumer goods and retail. E-commerce, in particular, is expected to surge, benefiting from the shift in consumer behavior towards online platforms.
Sustainable energy and electric mobility are other areas projected to gain momentum, aligning with global and national initiatives for a greener economy. This shift may influence the energy and automobile sectors, possibly leading to a revaluation of companies in these segments of the Nifty 50.
Infrastructure development remains a priority for the Indian government, which should continue to support the performance of related sectors like construction, cement, and metals. Additionally, as India's role on the international stage grows, sectors such as pharmaceuticals and chemicals are likely to receive a boost from increased exports and global partnerships.
Financially, with the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) monetary policy adapting to post-pandemic economic recovery and inflation rates, the financial sector may experience volatility. However, a stable banking system and robust regulatory framework should maintain investor confidence in the long term.
Overall, the Nifty 50 is expected to reflect these broad economic and social trends, with adaptability and resilience being key themes. While challenges such as global economic uncertainties and domestic policy shifts remain, the long-term outlook for the Nifty 50 remains optimistic, backed by strong fundamentals and growth prospects of the Indian economy.
In conclusion, the landscape of the Nifty 50 is a vibrant reflection of India's economic vitality and potential. As we have navigated through its composition, performance, and the various investment strategies that can be employed, it's clear that the index is not just a financial benchmark but also a testament to the country's growth story. With an eye on emerging trends and a commitment to adaptability, investors can look forward to participating in India's promising future. The Nifty 50, thus, stands as a beacon for both seasoned and aspiring investors, symbolizing the opportunities that lie in India’s dynamic market.

